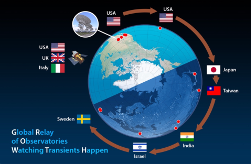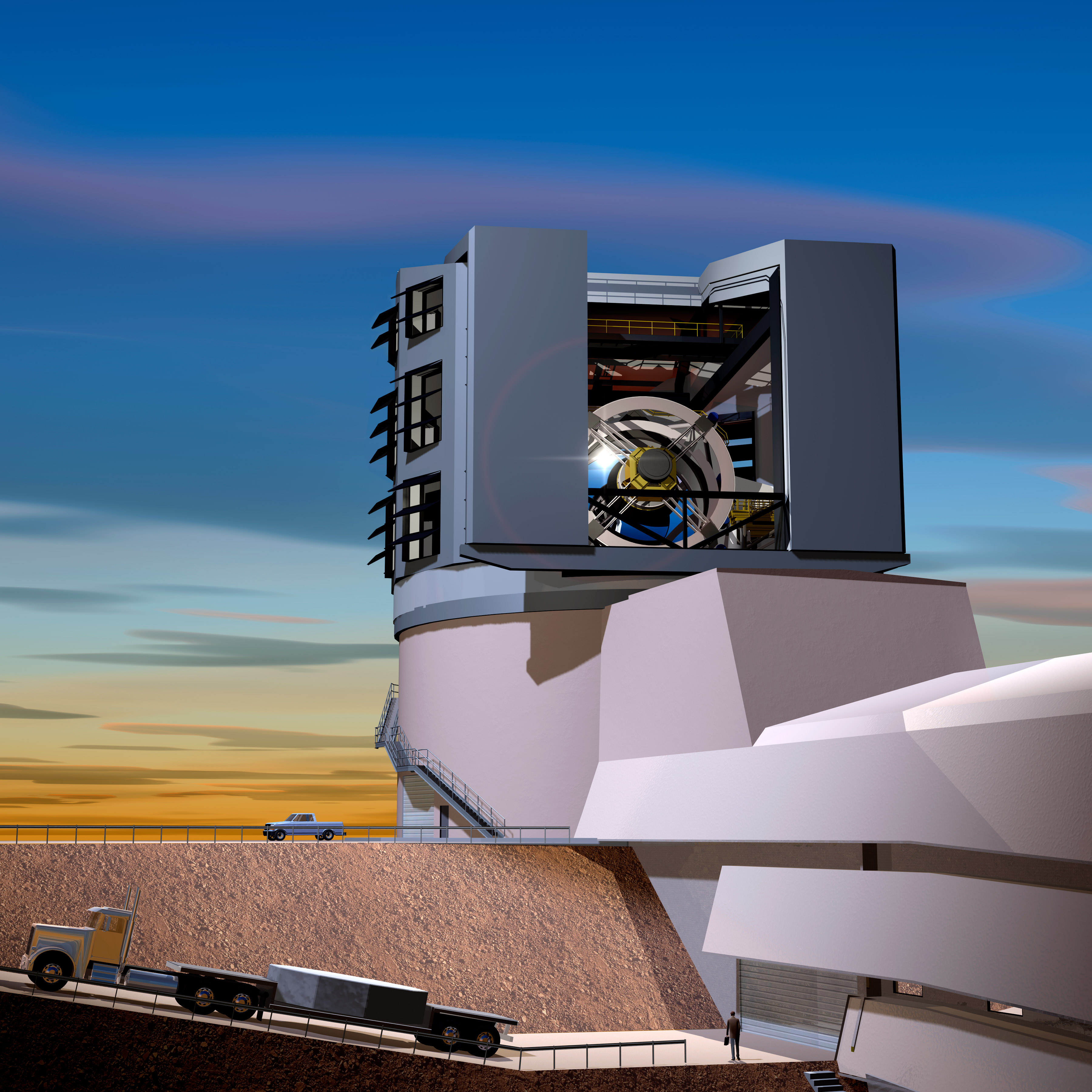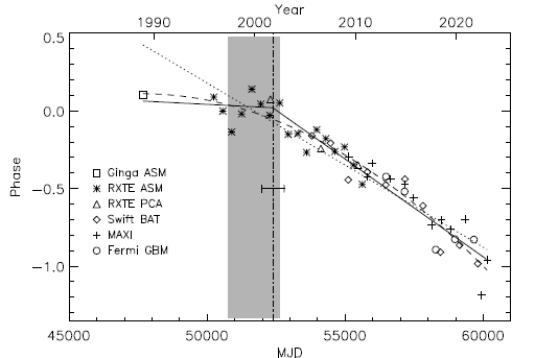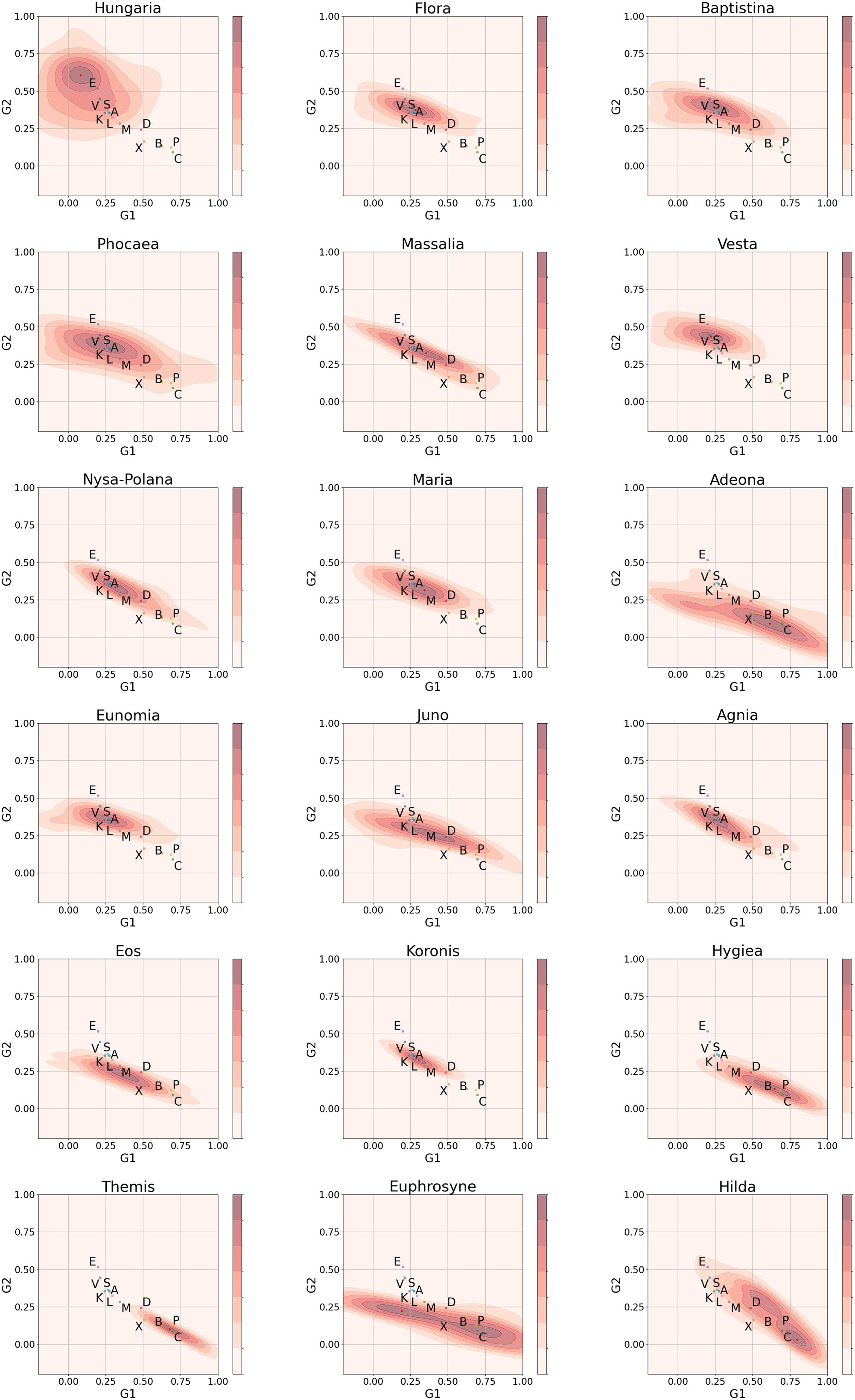





Recent Research + more
Honor+ more
- 恭賀本所 潘彥丞老師 通過114學年升等為副教授 (2025-06-13)
- 恭賀 本所碩士班戴辰宇同學榮獲2025年天文年會口頭報告特別獎、碩士班李昱星同學榮獲最佳學生壁報獎 (2025-05-19)
- 恭喜本所潘彥丞老師、陳婷琬老師榮獲「114年理學院推動科技研究發展學術活動獎勵」。 (2025-05-13)
- 恭賀 本所碩士班賴品憲同學獲得 113學年度第1學期國立中央大學優秀學生獎學金 (2025-03-18)
Academic Event
- No Meeting & Workshop
 Colloquium
Colloquium
- No recent colloquium
 Special Talk
Special Talk
- No recent Special Talk
- No recent Journal Club
Visiting Scholar + more
- No recent visiting scholar