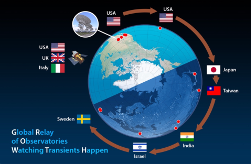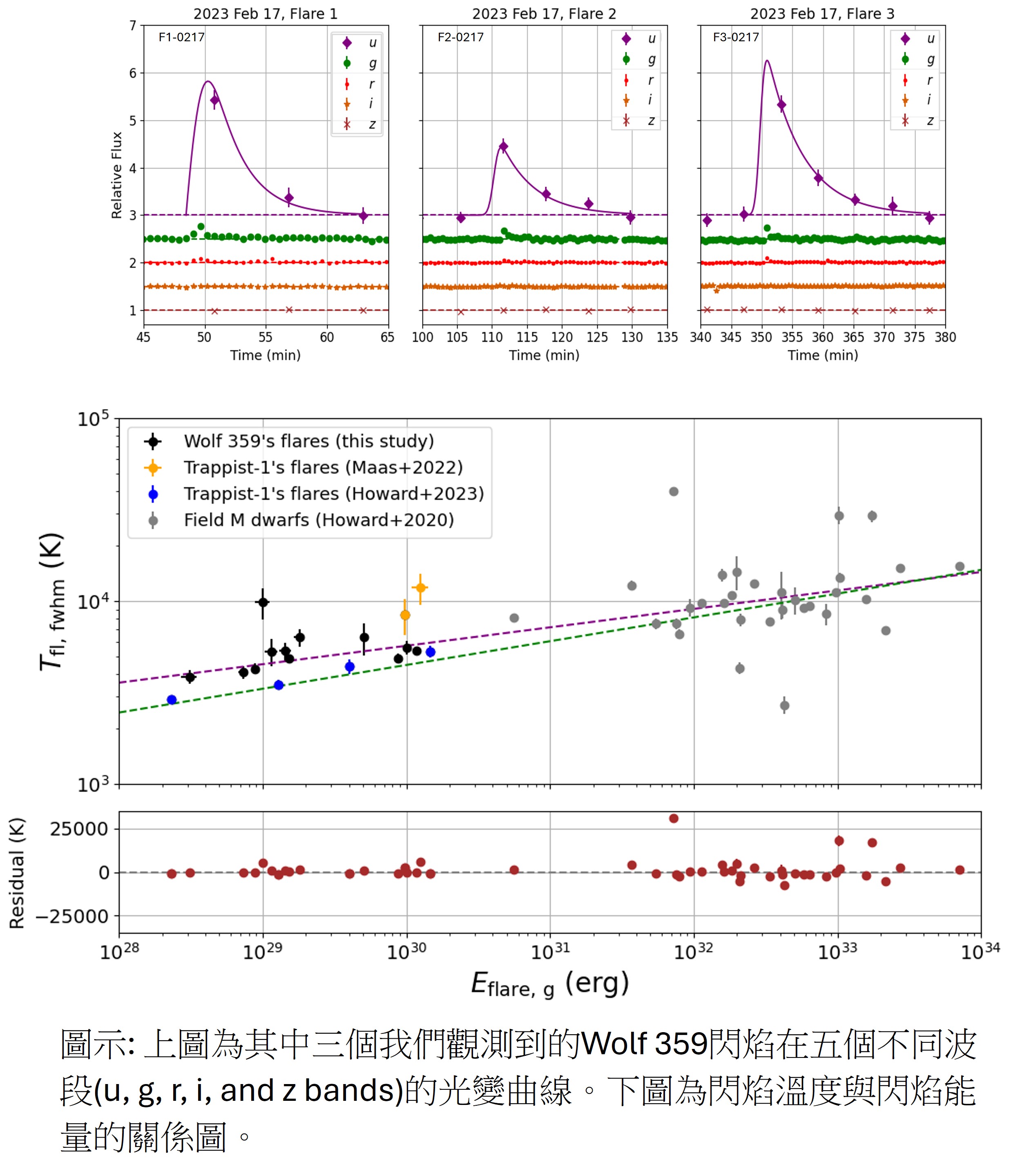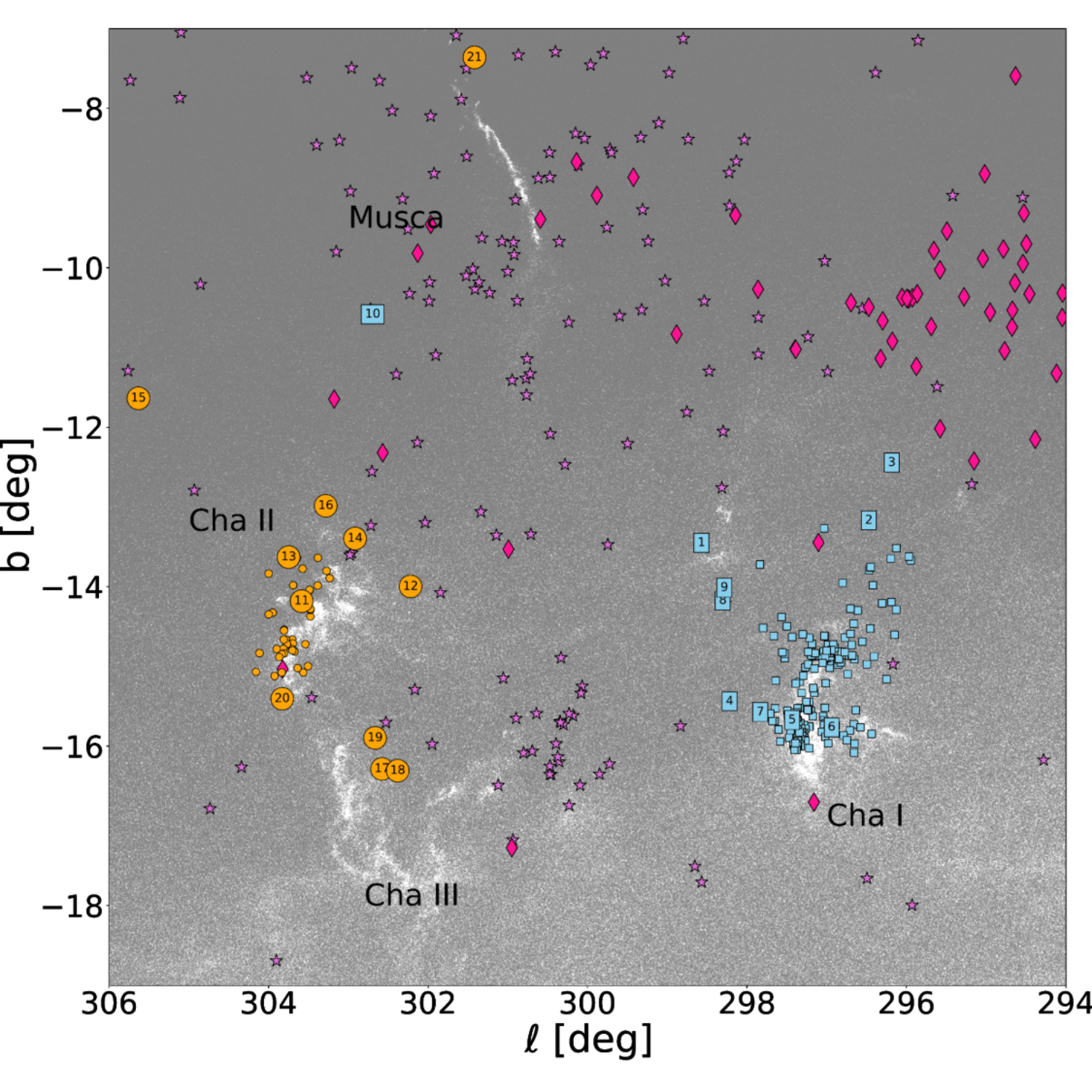








中大及其他天文台
News
- 2026-02-26
[天文所公告] 115學年度碩士班考試入學口試通知 - 2026-01-28
[天文所公告] 115學年度天文研究所博士班招生公告 - 2025-11-25
[天文所公告] 115學年度天文所碩士班考試招生 - 2025-11-07
[天文所公告] Google Workspace for Education 開始實施閒置帳戶政策 - 2025-10-20
[天文所公告] 115學年度天文研究所碩士班甄試入學口試公告
- No recent recruitment announcement
Recent Research + more
Honor+ more
- 恭喜本所張光祥同仁榮獲中央大學115年績優職員 (2026-01-27)
- 恭賀本所博士班柯亞莎 同學榮獲 2026年物理年會 AAPPS Award
Congratulations to Doctoral student Aiswarya Sankar Kachiprath for winning the AAPPS Award at the 2026 Annual Meeting of the Physical Society of Taiwan (2026-01-16) - 恭賀本所饒兆聰教授、潘彥丞副教授榮獲115年度本校學術研究傑出獎! (2025-12-30)
- 恭賀 本所博士班潘德吉(Bhattacharjee, Snehasish)同學獲得 114學年度第1學期國立中央大學優秀學生獎學金 (2025-11-14)
- 恭賀本所恭賀本所潘彥丞老師、陳婷琬老師榮獲中央大學114年優良論文貢獻獎。
恭賀本所恭賀本所木下大輔老師榮獲中央大學114年論文進步獎。 (2025-11-12)
Academic Event
- 2026-08-09
2026 Taiwan Lunar Symposium - 2026-04-15
International Workshop on Multiwavelength Studies of Supernovae, Kilonovae, and Gamma-Ray Bursts
 Colloquium
Colloquium
- No recent colloquium
 Special Talk
Special Talk
- No recent Special Talk
- Date: 2026-03-11
- Time: 12:00
- Location: S4-1013
- Speaker: Dr. Jen-Kai Hsu
- Title: TBD
Visiting Scholar + more
- Prof. Xinlin Li (2026-05-05~2026-05-11)
- Prof. Norbert Werner (2026-04-15~2026-04-15)
- Dr. Yuichi Harikane (2026-03-07~2026-03-15)